The Maze III
描述
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up (u), down (d), left (l) or right (r), but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction. There is also a hole in this maze. The ball will drop into the hole if it rolls on to the hole.
Given the ball position, the hole position and the maze, find out how the ball could drop into the hole by moving the shortest distance. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the hole (included). Output the moving directions by using 'u', 'd', 'l' and 'r'. Since there could be several different shortest ways, you should output the lexicographically smallest way. If the ball cannot reach the hole, output "impossible".
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The ball and the hole coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
Example 1:
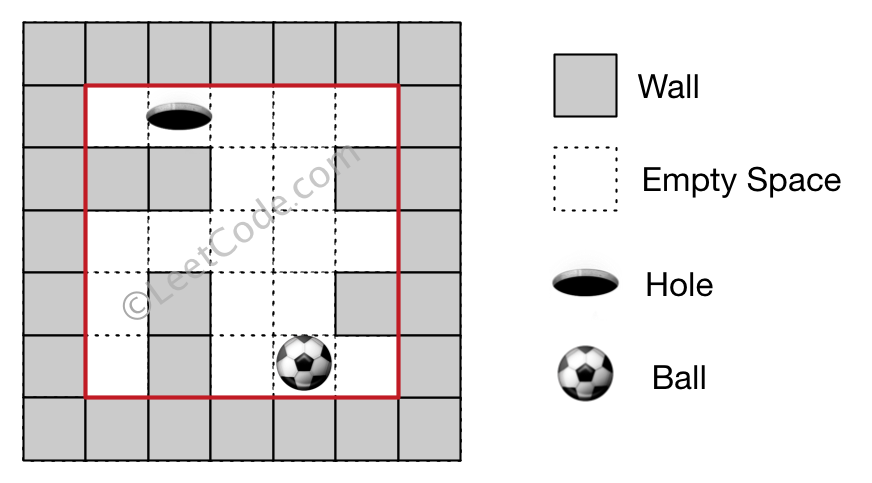
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0Input 2: ball coordinate (rowBall, colBall) = (4, 3)
Input 3: hole coordinate (rowHole, colHole) = (0, 1)Output: "lul"
Explanation: There are two shortest ways for the ball to drop into the hole.
The first way is left -> up -> left, represented by "lul".
The second way is up -> left, represented by 'ul'.
Both ways have shortest distance 6, but the first way is lexicographically smaller because 'l' < 'u'. So the output is "lul".
Example 2:
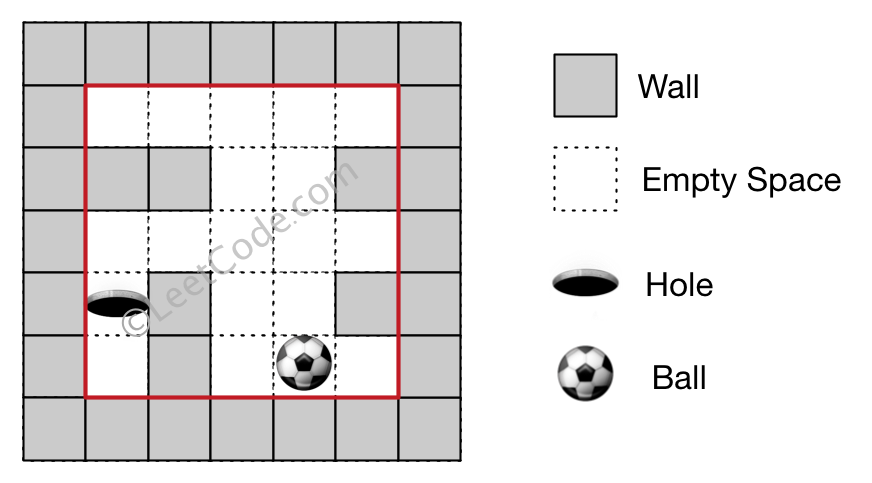
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0Input 2: ball coordinate (rowBall, colBall) = (4, 3)
Input 3: hole coordinate (rowHole, colHole) = (3, 0)Output: "impossible"
Explanation: The ball cannot reach the hole.
Note:
- There is only one ball and one hole in the maze.
- Both the ball and hole exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
- The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and the width and the height of the maze won't exceed 30.
分析
求最短路径,很显然,用 BFS。
代码
- Python
- Java
- C++
TODO
// The Maze III
// BFS
// Time complexity : O(m*n*max(m,n))
// Space complexity : O(mn)
public class Solution {
public String findShortestWay(int[][] maze, int[] ball, int[] hole) {
int m = maze.length, n = maze[0].length;
Point[][] points = new Point[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m * n; i++) points[i/n][i%n] = new Point(i/n, i%n);
Queue<Point> q=new LinkedList<>();
int[][] directions = {{-1,0}, {1,0}, {0,-1}, {0,1}};
String[] names=new String[] {"u", "d", "l", "r"};
final Function<Point, Boolean> stateIsValid = (Point p) ->
0 <= p.x && p.x < maze.length && 0 <= p.y && p.y < maze[0].length &&
maze[p.x][p.y] == 0 && (p.x!=hole[0] || p.y !=hole[1]);
final Function<Point, Boolean> stateIsTarget = (Point p) ->
p.x ==hole[0] && p.y ==hole[1];
final Function<Point, List<Point>> stateExtend = (Point p) -> {
List<Point> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Point newPoint = new Point(p);
while (stateIsValid.apply(newPoint)) {
newPoint.x +=directions[i][0];
newPoint.y +=directions[i][1];
newPoint.distance++;
}
if (!stateIsTarget.apply(newPoint)) { // check the hole
newPoint.x -= directions[i][0];
newPoint.y -= directions[i][1];
newPoint.distance--;
}
if (newPoint.compareTo(points[newPoint.x][newPoint.y]) < 0) {
newPoint.path += names[i];
result.add(newPoint);
}
}
return result;
};
points[ball[0]][ball[1]].distance = 0;
q.offer(points[ball[0]][ball[1]]);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Point p = q.poll();
List<Point> newStates = stateExtend.apply(p);
for (Point newState : newStates) {
q.offer(newState);
points[newState.x][newState.y] = newState;
}
}
return points[hole[0]][hole[1]].distance ==Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "impossible" : points[hole[0]][hole[1]].path;
}
static class Point implements Comparable<Point> {
int x, y; // coordinates
int distance; // distance between start and this point
String path; // path from start to this point
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.distance =Integer.MAX_VALUE;
this.path ="";
}
public Point(Point other) {
this.x = other.x;
this.y = other.y;
this.distance = other.distance;
this.path = other.path;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Point other) {
if (this.distance == other.distance) {
return this.path.compareTo(other.path);
} else {
return this.distance - other.distance;
}
}
}
}
TODO