LRU Cache
描述
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the following operations: get and set.
get(key) - Get the value (will always be positive) of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.
set(key, value) - Set or insert the value if the key is not already present. When the cache reached its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting a new item.
分析
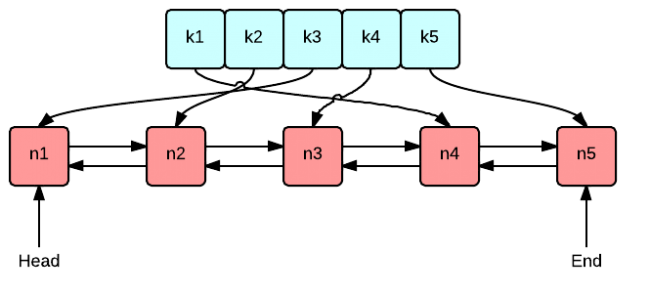
为了使查找、插入和删除都有较高的性能,这题的关键是要使用一个双向链表和一个 HashMap,因为:
- HashMap 保存每个节点的地址,可以基本保证在
O(1)时间内查找节点 - 双向链表能后在
O(1)时间内添加和删除节点,单链表则不行
具体实现细节:
- 越靠近链表头部,表示节点上次访问距离现在时间最短,尾部的节点表示最近访问最少
- 访问节点时,如果节点存在,把该节点交换到链表头部,同时更新 hash 表中该节点的地址
- 插入节点时,如果 cache 的 size 达到了上限 capacity,则删除尾部节点,同时要在 hash 表中删除对应的项;新节点插入链表头部
代码
C++的std::list 就是个双向链表,且它有个 splice()方法,O(1)时间,非常好用。
Java 中也有双向链表LinkedList, 但是 LinkedList 封装的太深,没有能在O(1)时间内删除中间某个元素的 API(C++的list有个splice(), O(1), 所以本题 C++可以放心使用splice()),于是我们只能自己实现一个双向链表。
本题有的人直接用 LinkedHashMap ,代码更短,但这是一种偷懒做法,面试官一定会让你自己重新实现。
- Java
- C++
- Python
// LRU Cache
// HashMap + Doubly Linked List
public class LRUCache {
private int capacity;
private Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> m;
private DLinkedList list;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
m = new HashMap<>();
list = new DLinkedList();
}
// Time Complexity: O(1)
public int get(int key) {
if (!m.containsKey(key)) return -1;
DLinkedNode node = m.get(key);
update(node);
return node.value;
}
// Time Complexity: O(1)
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (m.containsKey(key)){
DLinkedNode node = m.get(key);
node.value = value;
update(node);
} else {
DLinkedNode node = new DLinkedNode(key, value);
if (m.size() >= capacity){
DLinkedNode last = list.peekLast();
m.remove(last.key);
list.remove(last);
}
list.offerFirst(node);
m.put(key, node);
}
}
private void update(DLinkedNode node) {
list.remove(node);
list.offerFirst(node);
}
// Node of doubly linked list
static class DLinkedNode {
int key, value;
DLinkedNode prev, next;
DLinkedNode(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
// Doubly linked list
static class DLinkedList {
DLinkedNode head, tail;
int size;
DLinkedList() {
// head and tail are two dummy nodes
head = new DLinkedNode(0, 0);
tail = new DLinkedNode(0, 0);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
// Add a new node at head
void offerFirst(DLinkedNode node) {
head.next.prev = node;
node.next = head.next;
node.prev = head;
head.next = node;
size++;
}
// Remove a node in the middle
void remove(DLinkedNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
size--;
}
DLinkedNode peekLast() {
return tail.prev;
}
}
}
// LRU Cache
class LRUCache{
private:
// Node of doubly linked list
class DLinkedNode {
public:
int key, value;
DLinkedNode *prev=nullptr, *next=nullptr;
DLinkedNode(int key, int value) {
this->key = key;
this->value = value;
}
};
// Doubly linked list
class DLinkedList {
public:
DLinkedList() {
// head and tail are two dummy nodes
head = new DLinkedNode(0, 0);
tail = new DLinkedNode(0, 0);
head->next = tail;
tail->prev = head;
}
// Add a new node at head
void offerFirst(DLinkedNode *node) {
head->next->prev = node;
node->next = head->next;
node->prev = head;
head->next = node;
size++;
}
// Remove a node in the middle
void remove(DLinkedNode *node) {
if (node == nullptr) return;
node->prev->next = node->next;
node->next->prev = node->prev;
size--;
}
DLinkedNode* peekLast() {
return tail->prev;
}
private:
DLinkedNode *head, *tail;
int size;
};
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) {
this->capacity = capacity;
}
// Time Complexity: O(1)
int get(int key) {
if (m.find(key) == m.end()) return -1;
DLinkedNode *node = m[key];
update(node);
return node->value;
}
// Time Complexity: O(1)
void put(int key, int value) {
if (m.find(key) != m.end()){
DLinkedNode *node = m[key];
node->value = value;
update(node);
} else {
DLinkedNode *node = new DLinkedNode(key, value);
if (m.size() >= capacity){
DLinkedNode *last = list.peekLast();
m.erase(last->key);
list.remove(last);
}
list.offerFirst(node);
m[key] = node;
}
}
void update(DLinkedNode *node) {
list.remove(node);
list.offerFirst(node);
}
private:
int capacity = 0;
unordered_map<int, DLinkedNode*> m;
DLinkedList list;
};
# LRU Cache
# OrderedDict
class LRUCache:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.cache = OrderedDict()
# Time Complexity: O(1)
def get(self, key):
if key in self.cache:
value = self.cache.pop(key)
self.cache[key] = value
return value
else: return -1
# Time Complexity: O(1)
def put(self, key, value):
if key in self.cache:
self.cache.pop(key)
self.cache[key] = value
if len(self.cache) > self.capacity:
self.cache.popitem(last=False)